Vulnerability Description: Use of GET Request Method With Sensitive Query Strings - CWE-598
Software Version: 1.6.4
NIST: https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-31842
CVSS: 8.8
Severity: High
Credits: Luca Carbone, Fabio Romano, Federico Draghelli, Massimiliano Brolli
The web application inserts the access token of an authenticated user inside GET requests.
Step-by-step instructions and PoC
The query string for the URL could be saved in the browser's history, passed through Referers to other web sites, stored in web logs, or otherwise recorded in other sources. If the query string contains sensitive information such as session identifiers, then attackers can use this information to launch further attacks. Since the access token in sent in GET requests, this vulnerability could lead to complete account takeover.
Below are the evidences with the vulnerability details and the payloads used.
In the following screenshot there is an example of a GET request that contains the access token in the query string. This vulnerability is applicable to almost every functionality of the web application.
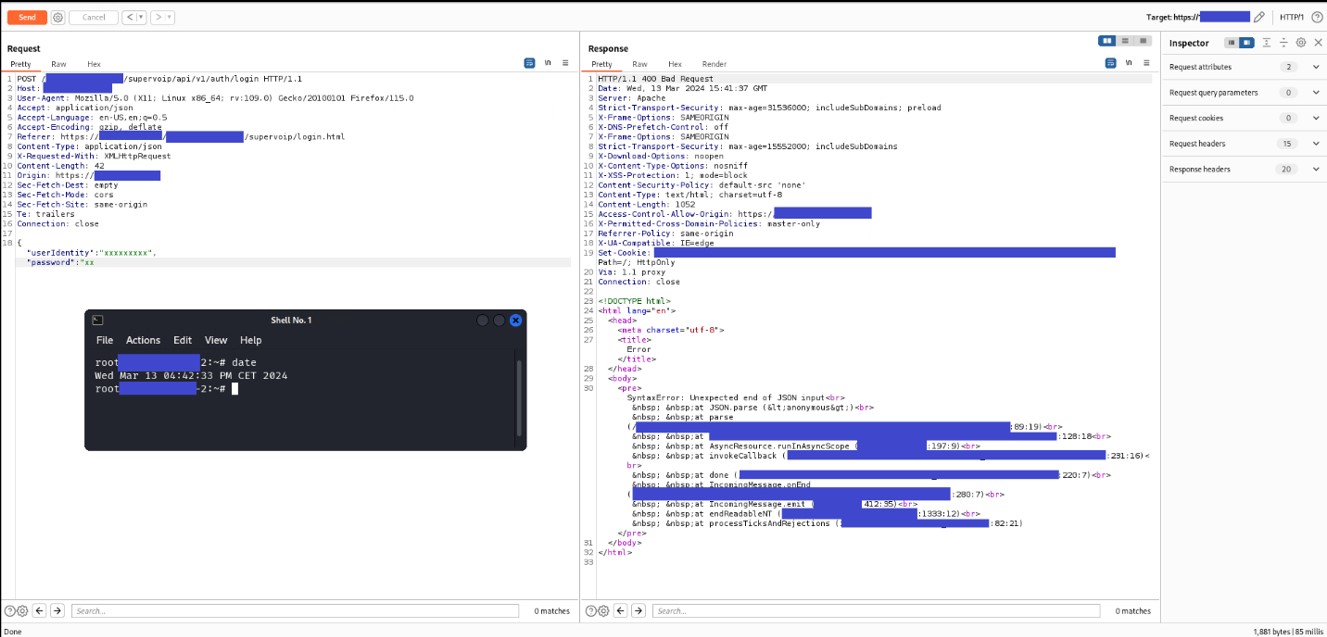
Figure 2 - The access token is in the URL of the GET request
Security Impact
An attacker that is able to read the token could access the web application as another user.